Material Selection for Butt Weld Fittings Choosing the right material is the first step in selecting...
Alloy Fittings: Types, Benefits, and Applications

Understanding Alloy Fittings
Alloy fittings are precision-engineered components used to join, adapt, or redirect pipes and tubes. They are manufactured from metallic alloys to deliver strength, corrosion resistance, and long-term durability in high-demand environments. Unlike standard fittings, alloys can withstand extreme temperatures, mechanical stress, and chemically aggressive media.
Key Types and Their Functional Roles
The design of alloy fittings varies to meet functional and operational requirements. Selecting the correct type ensures optimal flow, pressure handling, and system longevity.
- Elbows: Change flow direction with minimal turbulence; essential in pipelines requiring 45° or 90° turns.
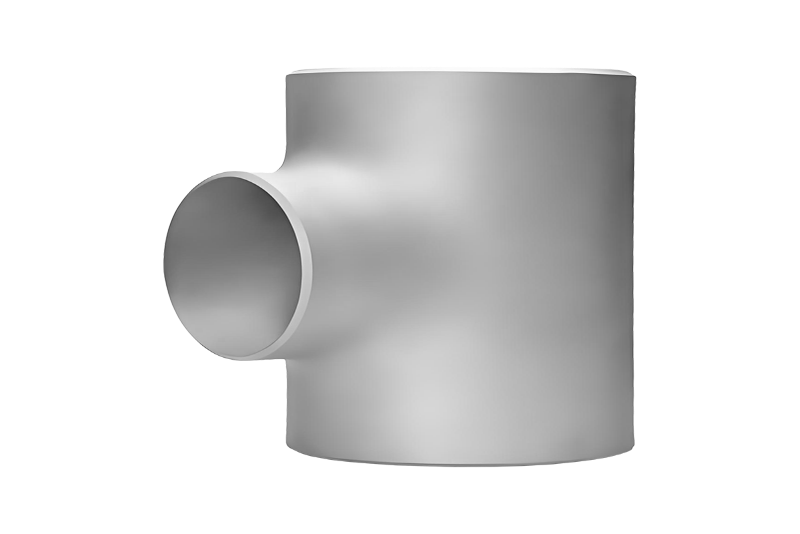
- Tees and Crosses: Enable multi-branch connections, crucial in complex distribution systems.
- Reducers: Smoothly transition pipe diameters, minimizing pressure drop and turbulence.
- Couplings and Unions: Provide straight connections with leak-proof sealing and easy disassembly.
- Flanges: Facilitate removable connections for maintenance and inspection in high-pressure applications.
Material Selection and Alloy Science
The alloy composition determines mechanical performance, corrosion resistance, and operational limits. Common alloys include stainless steel, nickel-based alloys, brass, aluminum, and titanium blends. Each has unique properties suited to specific industrial environments.
| Alloy | Mechanical Strength | Corrosion Resistance | Applications |
| 304/316 Stainless Steel | High tensile & yield strength | Excellent, even in acidic or saline environments | Chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing |
| Nickel-based Alloys | Extremely high strength at elevated temperatures | Resistant to oxidation and acidic corrosion | Aerospace, power plants, oil & gas |
| Aluminum Alloys | Lightweight yet durable | Moderate, suitable for mild environments | Automotive, aerospace, HVAC systems |
| Brass | Moderate strength, excellent machinability | Excellent, resists rust and mineral deposits | Plumbing, water treatment, decorative fixtures |
Performance Considerations in Industrial Applications
Selecting an alloy fitting requires evaluating multiple performance factors. Engineers must balance mechanical strength, thermal tolerance, chemical compatibility, and ease of maintenance.
- Pressure Ratings: Ensure the fitting withstands maximum system pressure without deformation or failure.
- Temperature Range: Alloy composition must maintain structural integrity under operating heat and cold.
- Chemical Resistance: Avoid corrosion or degradation in contact with transported media.
- Wear and Fatigue: Repeated stress, vibration, and movement demand high fatigue resistance.
Installation, Maintenance, and Longevity
Proper installation and maintenance are critical for maximizing the life of alloy fittings. Key practices include:
- Using appropriate torque specifications to prevent over-tightening or thread damage.
- Applying anti-corrosion coatings or sealants in aggressive environments.
- Regular inspection for leaks, cracks, or wear using non-destructive testing methods.
- Periodic cleaning to remove deposits and prevent localized corrosion.
Industry-Specific Applications
Alloy fittings are essential across industries where reliability and durability are non-negotiable. Typical sectors include:
- Oil & Gas: High-pressure pipelines, refineries, and offshore installations.
- Aerospace & Automotive: Lightweight fittings for fuel, hydraulic, and cooling systems.
- Chemical & Pharmaceutical: Corrosion-resistant connections for reactive and high-purity fluids.
- Water & HVAC: Durable fittings for plumbing, heating, and cooling networks.

Stay Informed About Our Recent Events

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى