Material Selection for Butt Weld Fittings Choosing the right material is the first step in selecting...
Forged Fittings: Applications, Selection Guide, and Key Advantages

1. What Are Forged Fittings and Why They Matter in Industrial Piping?
Forged fittings are high-strength components used to connect, terminate, or control the flow in piping systems that operate under extreme pressure and temperature. Their durability comes from the forging process, where metal is shaped using compressive force, resulting in a refined grain structure and exceptional mechanical integrity. Industries such as oil and gas, petrochemical, power generation, and heavy machinery rely on forged fittings to ensure leak-free, long-lasting pipe systems.
Compared to other connection methods, forged fittings offer superior fatigue resistance, dimensional accuracy, and tolerance to vibration and corrosion. Because safety and performance are paramount in demanding operating environments, forged fittings remain a critical component in system reliability.
2. Key Types of Forged Fittings and Their Practical Functions
2.1 Socket Weld Fittings
Socket weld forged fittings are commonly used for small-diameter, high-pressure pipelines. These fittings allow the pipe to be inserted into a recessed area before welding, creating a strong and permanent joint. They are preferred when leakage must be minimized, such as in steam, hydraulic, and chemical transport lines.
- Provide excellent structural integrity for high-pressure systems.
- Reduce stress concentrations due to internal bore alignment.
- Ideal for vibration-intensive applications.
2.2 Threaded Forged Fittings
Threaded forged fittings use screw-type connections, making them suitable for low- to medium-pressure lines and systems requiring quick installation or dismantling. These fittings are widely used where welding is inconvenient or prohibited, such as explosive environments or small-scale maintenance tasks.
- Allow easy assembly and disassembly without welding.
- Reduce downtime during repairs and adjustments.
- Suitable for small-pipe utility networks.
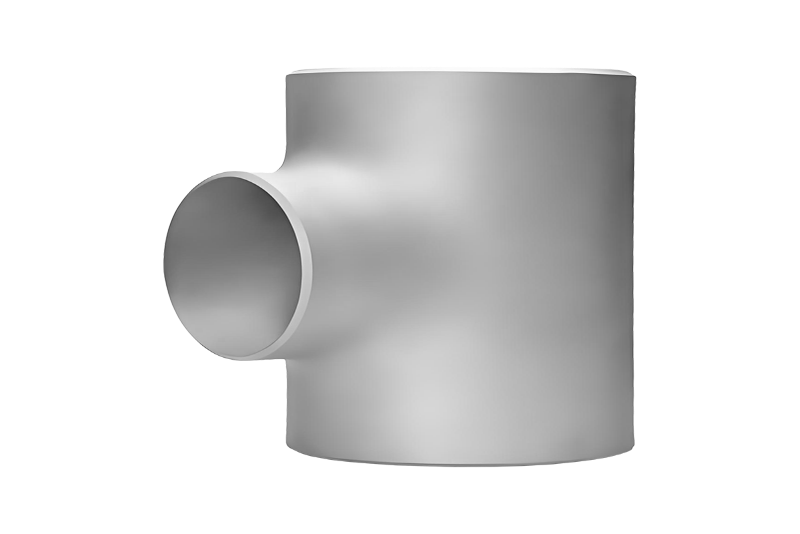
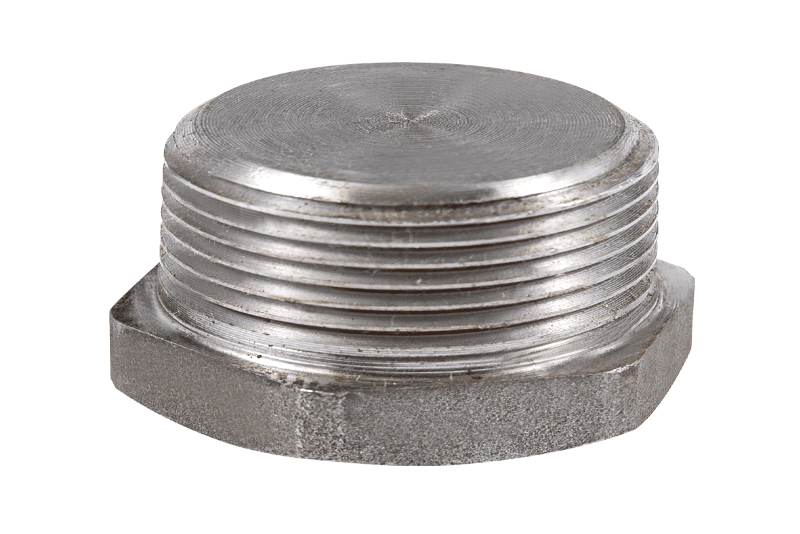
2.3 Common Shapes and Their Uses
Forged fittings come in various shapes to perform precise functions in complex pipe routing. Each type is designed to handle specific flow direction, pressure requirements, and connection demands.
| Elbows | Change flow direction (45° or 90°) in confined spaces. |
| Tees | Distribute fluid into two lines or integrate branch pipelines. |
| Couplings | Join two pipes to extend length or repair sections. |
| Caps and Plugs | Terminate pipeline ends safely and securely. |
| Unions | Enable frequent disassembly without damaging the pipeline. |
3. Material Selection for Forged Fittings and Their Performance Differences
The performance and lifespan of forged fittings largely depend on the selected material. Each material type offers unique advantages for specific pressure ratings, temperatures, and fluid properties. Choosing correctly reduces maintenance costs and enhances safety.
- Carbon Steel: Ideal for high-pressure systems transporting oil, gas, and steam. Offers good toughness and affordability.
- Stainless Steel: Provides excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for chemical plants, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
- Alloy Steel: Designed for extreme conditions, including high temperatures and aggressive media.
- Duplex Steel: Combines strong corrosion resistance with higher mechanical strength, reducing wall thickness requirements.
Selecting the correct material also involves considering compatibility with the pipeline medium, the likelihood of corrosion, mechanical shock, and industry standards such as ASME, ASTM, and API.
4. Forged Fittings vs. Cast Fittings: Which Is Better for Your Application?
Although forged and cast fittings may appear similar externally, their internal structure and performance differ significantly. Forged fittings are preferable for critical applications due to their higher strength and reliability, while cast fittings may suit lower-pressure or cost-sensitive environments.
| Feature | Forged Fittings | Cast Fittings |
| Strength | Very high due to grain refinement | Moderate strength, more porous |
| Pressure Rating | Suitable for extreme pressure | Used for medium- to low-pressure |
| Reliability | Highly reliable, low failure rate | Possibility of casting defects |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower cost |
For critical systems where safety or operational demands are high, forged fittings remain the preferred choice due to their reliability and structural performance.
5. Practical Tips for Selecting the Right Forged Fittings
Selecting forged fittings involves more than matching size and pressure rating. Engineers and procurement specialists must evaluate environmental factors, long-term maintenance expectations, and compliance with international standards. Below are actionable considerations that help ensure proper selection.
- Verify pressure class (e.g., 3000#, 6000#, 9000#) based on system design.
- Check material compatibility with the transported fluid to avoid corrosion and contamination.
- Account for temperature effects, especially in steam or high-temperature gas systems.
- Ensure that fittings meet ASME or API specifications for dimensional accuracy and performance.
- Choose manufacturers with proven fabrication and testing capabilities, such as hardness tests, hydrostatic tests, and non-destructive examination.
By combining proper material choice, structural design, and usage environment evaluation, you can maximize the service life of forged fittings while maintaining cost-effectiveness and operational reliability.

Stay Informed About Our Recent Events

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى