Material Selection for Butt Weld Fittings Choosing the right material is the first step in selecting...
What is a Butt Weld Reducing Tee and How Is It Used in Piping Systems?

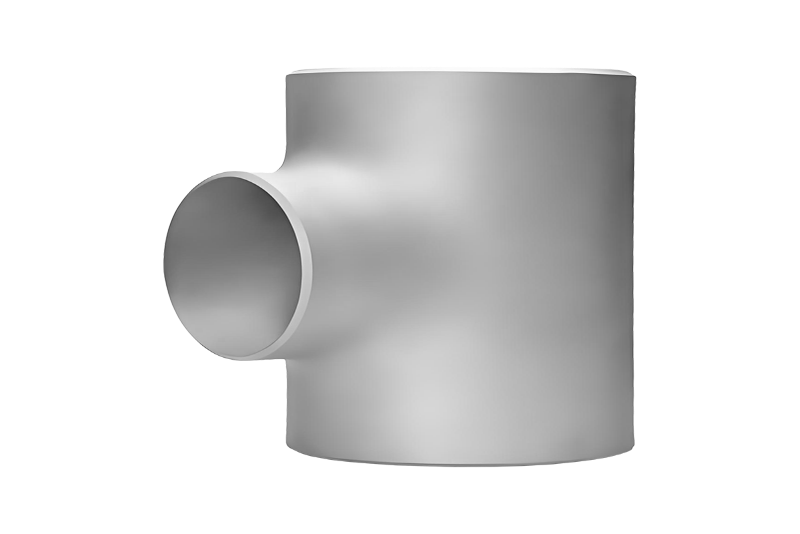
A butt weld reducing tee is a type of pipe fitting used in piping systems to connect three sections of pipe where one branch has a smaller diameter than the main run. Unlike equal tees, where all three outlets share the same size, a reducing tee allows a change in pipe diameter while maintaining a smooth, welded connection. The term “butt weld” refers to the welding method, in which the fitting is welded directly to the pipe ends using full-penetration welds.
These fittings are widely used in high-pressure, high-temperature, and critical service applications because butt welding creates a strong, leak-resistant joint. Butt weld reducing tees are commonly manufactured according to international standards and are available in a wide range of sizes, schedules, and materials to suit different industrial requirements.
Key Structural Features of a Butt Weld Reducing Tee
The defining feature of a butt weld reducing tee is its three openings: two aligned openings forming the main run and one perpendicular branch with a smaller nominal diameter. All ends are prepared with bevels to facilitate butt welding, ensuring proper weld penetration and strength.
The internal geometry of the fitting is designed to allow relatively smooth flow transition from the larger pipe to the smaller branch. This minimizes turbulence and pressure drop, which is especially important in process piping systems where flow efficiency and stability are critical.
How Butt Weld Reducing Tees Work in Piping Systems
In a piping system, a butt weld reducing tee is used to divert part of the fluid flow from a main pipeline into a smaller branch line. This branch may supply equipment, instruments, or secondary pipelines that require a lower flow rate or smaller pipe size.
Because the fitting is welded directly to the pipes, it becomes an integral part of the pipeline. This welded construction provides excellent mechanical strength and eliminates potential leak paths that may exist in threaded or socket-weld connections. As a result, butt weld reducing tees are preferred in systems transporting hazardous, flammable, or high-value fluids.

Common Materials Used for Butt Weld Reducing Tees
Material selection plays a crucial role in the performance and service life of a butt weld reducing tee. The material must be compatible with the conveyed fluid, operating temperature, pressure, and environmental conditions.
- Carbon steel, commonly used for general industrial and oil and gas applications.
- Stainless steel, offering excellent corrosion resistance for chemical and food processing systems.
- Alloy steel, suitable for high-temperature and high-pressure environments such as power plants.
- Duplex and super duplex stainless steel for aggressive and corrosive offshore or marine conditions.
Choosing the correct material ensures not only compliance with design codes but also long-term reliability of the piping system.
Manufacturing Standards and Dimensions
Butt weld reducing tees are typically manufactured according to recognized standards such as ASME B16.9, MSS SP-75, or EN standards. These standards define dimensions, tolerances, wall thickness, and testing requirements, ensuring interchangeability and consistent quality.
The wall thickness of the tee usually matches the schedule of the connected pipes, such as Schedule 40, Schedule 80, or higher. This consistency helps maintain uniform strength throughout the piping system and simplifies welding and inspection procedures.
Typical Applications of Butt Weld Reducing Tees
Butt weld reducing tees are used across a wide range of industries where durability and safety are paramount. Their ability to handle demanding service conditions makes them a standard choice in critical piping networks.
- Oil and gas pipelines for branching flow to auxiliary lines or equipment.
- Chemical processing plants handling corrosive or hazardous fluids.
- Power generation facilities, including thermal and nuclear plants.
- Water treatment and desalination systems requiring reliable welded connections.
Butt Weld Reducing Tee vs Equal Tee
The main difference between a butt weld reducing tee and an equal tee lies in the branch size. An equal tee has three outlets of the same diameter, while a reducing tee has a smaller branch. This distinction directly affects how flow is distributed and controlled within the piping system.
Reducing tees are often chosen when space, cost, or flow requirements make it impractical to use equal tees with reducers. By combining branching and size reduction in a single fitting, reducing tees simplify system design and reduce the number of weld joints.
Installation and Welding Considerations
Proper installation is essential to ensure the performance of a butt weld reducing tee. Accurate alignment of the pipes and fitting is critical to prevent stress concentration and welding defects. Qualified welders and approved welding procedures are typically required for these fittings.
Post-weld inspection methods such as radiographic testing or ultrasonic testing are often applied to verify weld integrity. These inspections help detect internal defects and ensure compliance with applicable codes and safety standards.
Advantages of Using Butt Weld Reducing Tees
The popularity of butt weld reducing tees is driven by their performance advantages in demanding applications. Their welded construction provides superior strength and reliability compared to other connection types.
- High structural integrity suitable for high-pressure systems.
- Smooth internal bore that reduces turbulence and pressure loss.
- Long service life with minimal maintenance requirements.
How to Select the Right Butt Weld Reducing Tee
Selecting the appropriate butt weld reducing tee requires careful evaluation of operating conditions and system requirements. Key factors include pipe sizes, pressure rating, temperature range, material compatibility, and applicable design codes.
Working with experienced manufacturers or suppliers can help ensure the fitting meets both technical specifications and regulatory standards. Proper selection reduces installation issues and enhances the overall safety and efficiency of the piping system.
Conclusion: The Role of Butt Weld Reducing Tees in Modern Piping
A butt weld reducing tee is a critical component in many industrial piping systems, enabling efficient branching while maintaining strength and reliability. Its welded design, material versatility, and compliance with international standards make it suitable for some of the most demanding applications.
By understanding how butt weld reducing tees function and where they are best applied, engineers and project managers can design safer, more efficient piping networks that perform reliably over long service periods.
Stay Informed About Our Recent Events

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى